Purpose of the Chapter
The primary purpose of this opening chapter is to lay a foundational understanding of Information Technology (IT) Governance, a critical aspect of contemporary organizational management. By establishing a solid groundwork, the chapter aims to provide readers with a comprehensive view of IT Governance’s pivotal role in aligning IT strategy with business objectives, ensuring efficient resource utilization, and mitigating IT-related risks.
Today, IT plays a central role in almost every aspect of an organization. However, the rapid evolution of technology, coupled with its increasing complexity, poses significant challenges for businesses. This chapter addresses these challenges by dissecting the essence of IT Governance and elucidating its necessity in the modern corporate landscape.
Elucidating the Concept:
The chapter begins by presenting a clear and concise definition of IT Governance. It is essential to understand that IT Governance is not just about managing IT systems but is a strategic framework that guides and aligns IT usage with business goals and objectives. To illustrate this, consider a multinational corporation that leverages IT Governance to ensure that its IT investments directly contribute to its global expansion goals, leading to improved business efficiency and market competitiveness.
Scope and Relevance:
Beyond definition, the chapter explores the scope and relevance of IT Governance in various business contexts. For instance, in the banking sector, IT Governance is instrumental in managing risks associated with digital transactions and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. Similarly, in healthcare, IT Governance plays a crucial role in securing patient data and enhancing the quality of care through technology.
Historical Perspective:
A historical perspective is provided to help readers understand the evolution of IT Governance. The chapter will draw parallels between significant technological advancements and shifts in IT Governance practices. For example, the advent of cloud computing significantly altered how organizations govern their IT resources, emphasizing more on data security and regulatory compliance.
Practical Insights:
The chapter also offers practical insights into the application of IT Governance principles. This includes real-world examples from renowned companies that have successfully implemented IT Governance frameworks, highlighting the tangible benefits they reaped in enhanced operational efficiency, cost savings, and improved risk management.
Setting the Stage:
This chapter sets the stage for deeper exploration into various facets of IT Governance, such as risk management, strategic alignment, performance measurement, and the role of various frameworks like COBIT, ITIL, and ISO/IEC 38500. The intention is to build a comprehensive narrative that gradually unfolds the complexities and nuances of IT Governance, preparing the reader for more advanced topics in subsequent chapters.
For Whom This Chapter Is Intended:
This chapter is designed to cater to a broad spectrum of readers, from CIOs and IT Leaders to IT professionals and students to business leaders and managers. Whether the reader is a seasoned IT executive, an aspiring IT manager, or a business leader looking to understand the impact of IT on organizational success, this chapter serves as a crucial stepping stone in understanding the strategic importance of IT Governance.
In closing, the purpose of this chapter is not just to inform but to enlighten and empower readers with the knowledge and understanding necessary to navigate the complex world of IT Governance. Through a blend of theoretical insights, practical examples, and historical context, the chapter aims to provide a solid foundation upon which the rest of the book will build.
Overview of IT Governance
IT Governance is a pivotal aspect of organizational strategy, particularly in an era where information technology is not just an enabler but a driver of business innovation and growth. For CIOs and IT leaders, understanding the breadth and depth of IT Governance is crucial to aligning technology initiatives with business goals, ensuring robust risk management, and delivering value through IT investments.
At its essence, IT Governance encompasses the frameworks and processes that guide and control the IT-related decisions and actions of an organization. This domain extends beyond mere technology management; it interweaves IT with the overall business strategy, ensuring that every IT decision and investment contributes to the broader organizational objectives.
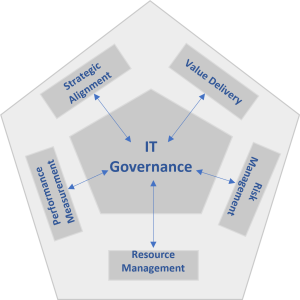
The realm of IT Governance is multifaceted, involving strategic alignment, value delivery, risk management, resource management, and performance measurement:
- Strategic Alignment: This involves synchronizing IT strategy with business strategy to ensure that IT supports and enhances business objectives.
- Value Delivery: IT must not only support but actively drive business value, necessitating a focus on optimizing costs and demonstrating the tangible benefits of IT investments.
- Risk Management: A crucial aspect for IT leaders, involving the protection of IT assets, effective disaster recovery planning, and ensuring continuity of operations.
- Resource Management: This includes the optimal allocation and management of IT resources—both human and technical—to support the organization’s goals.
- Performance Measurement: Monitoring and evaluating IT performance through relevant metrics and key performance indicators is essential to assess and steer IT’s contribution to the business.
IT Governance also heavily relies on established frameworks and standards like COBIT, ITIL, and ISO/IEC 38500. These frameworks offer structured and proven approaches for implementing effective IT Governance, aiding organizations in achieving strategic IT-business alignment, operational excellence, and compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
The role of IT Governance has evolved. It is no longer just about ensuring IT efficiency and effectiveness; it’s about fostering a technology-driven culture that can adapt to rapid technological changes, mitigate IT-related risks, and harness technology for strategic advantage. For CIOs and IT leaders, mastering IT Governance is not optional but a fundamental requirement to navigate the complex digital landscape, drive innovation, and create sustainable business value.