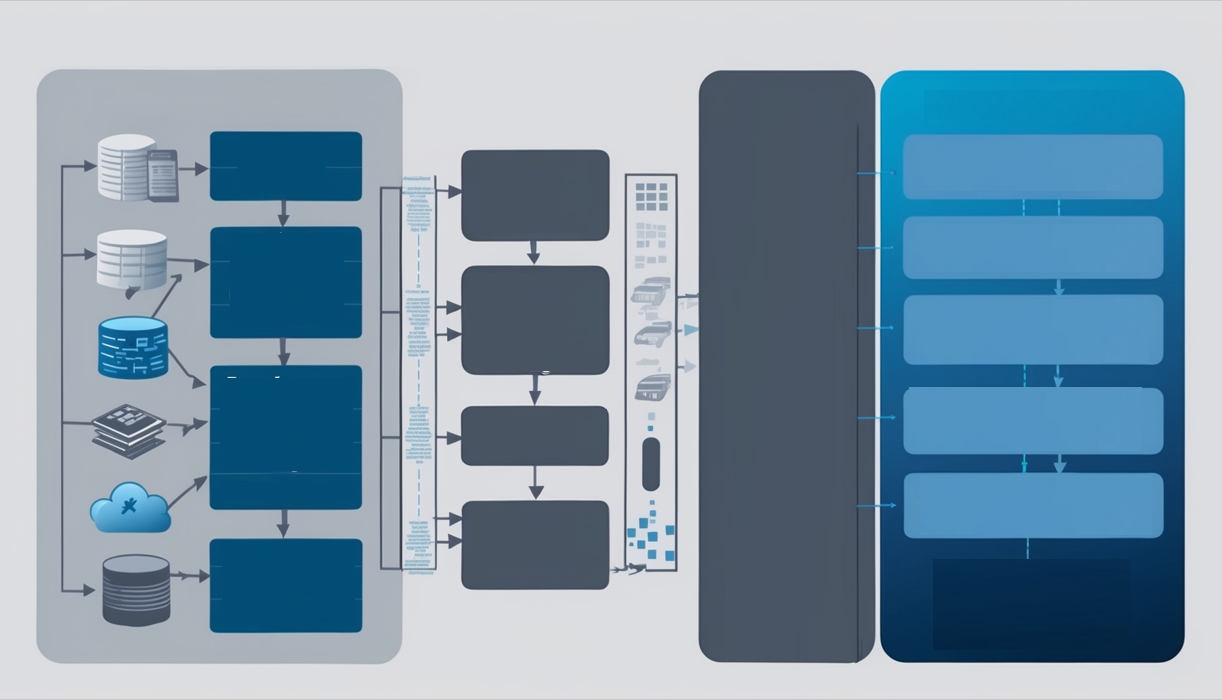
Big Data refers to the massive volume of structured and unstructured data generated by various sources, such as social media, sensors, digital devices, and business transactions. The term “Big Data” is often used to describe datasets that are too large, complex, or dynamic to be processed, analyzed, and managed using traditional data processing tools and techniques. Big Data is characterized by the 5Vs: Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value.
- Volume: This refers to the sheer amount of data generated and stored by organizations and individuals. Big Data often involves terabytes or even petabytes of data, requiring advanced storage and processing solutions.
- Velocity: Big Data is often generated and processed in real-time or near-real-time, necessitating powerful tools and techniques to handle the rapid flow of data.
- Variety: Big Data encompasses data in various formats, such as structured data (e.g., databases), unstructured data (e.g., text, images, videos), and semi-structured data (e.g., XML files).
- Veracity: Ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of Big Data is crucial, as poor data quality can lead to incorrect insights and decision-making.
- Value: The true potential of Big Data lies in its ability to generate valuable insights, drive innovation, and enable better decision-making for organizations.
Big Data technologies and tools, such as Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases, have been developed to address the challenges associated with storing, processing, and analyzing large and complex datasets. Big Data analytics involves the use of advanced techniques, such as machine learning, data mining, and predictive analytics, to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and trends within the data.
Big Data applications span across various industries and sectors, including:
- Healthcare: Big Data can improve patient care, enhance medical research, and enable personalized medicine by analyzing electronic health records, genomics data, and medical imaging.
- Finance: Financial institutions use Big Data to detect fraud, manage risk, and enhance customer service by analyzing transaction data, market trends, and customer behavior.
- Retail: Retailers leverage Big Data to optimize supply chain management, personalize marketing efforts, and improve customer experience by analyzing sales data, customer feedback, and social media trends.
- Manufacturing: Big Data can enhance quality control, optimize production processes, and enable predictive maintenance by analyzing sensor data, machine logs, and production metrics.
- Government: Governments can use Big Data to enhance public services, optimize resource allocation, and inform policy-making by analyzing population data, social trends, and economic indicators.
- Smart Cities: Big Data can improve urban planning, transportation, and resource management in smart cities by analyzing data from IoT devices, sensors, and social media.
The potential benefits of Big Data are significant, but there are also challenges and concerns, such as data privacy, security, and ethical considerations. Organizations must adopt responsible data management practices and adhere to relevant regulations to ensure the appropriate use and protection of Big Data.
The Big Data category within our CIO Reference Library is a comprehensive collection of resources, articles, and insights designed to help CIOs and IT executives navigate the complex world of big data management, analytics, and implementation. This category focuses on providing IT leaders with the knowledge and tools needed to effectively harness the power of big data, enabling them to make better-informed decisions, drive innovation, and create a competitive edge for their organizations.
In this category, you will find valuable information on a wide range of topics related to big data, including:
- Understanding big data fundamentals, including the key concepts, technologies, and platforms for data storage, processing, and analytics.
- Developing and implementing big data strategies aligning with your organization’s objectives and technology landscape.
- Selecting the right big data tools, solutions, and partners to support your organization’s data management and analytics needs.
- Designing, deploying, and managing scalable, secure, and compliant big data infrastructure and architectures.
- Leveraging advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and AI, to extract actionable insights from your organization’s big data assets.
- Implementing data governance and privacy best practices to ensure the responsible and ethical use of big data.
- Staying up-to-date with the latest trends, research, and innovations in the big data landscape.
By exploring the Big Data category, IT leaders can better understand the challenges and opportunities associated with managing and utilizing large-scale data assets. This knowledge will enable you to develop and execute effective big data initiatives that drive significant value, efficiency, and innovation for your organization.