I. Introduction
Imagine a future arriving sooner than you think: According to Gartner, by 2025, organizations harnessing autonomous generative AI systems will outperform their competitors by at least 25% in both productivity and decision-making accuracy. In practical terms, this means a significant leap beyond automating mundane, repetitive tasks—organizations will be leveraging AI to independently make strategic decisions and proactively respond to complex challenges and continuously innovate. Historically, CIOs have led the charge in adopting technology primarily to streamline operational processes and reduce manual workloads. But today, as generative AI rapidly evolves, the shift from automation toward genuine autonomy is fundamentally redefining the very essence of the CIO role. This transformation requires CIOs to understand and integrate advanced AI technologies and adopt new leadership archetypes, strategic priorities, and ethical responsibilities. In this blog post, we will explore precisely how generative AI is changing the role of CIOs, why these changes are occurring, and what CIOs must do to prepare effectively for this new era of technological autonomy.
II. Clarifying Key Concepts
Automation vs. Autonomy
To clearly understand how generative AI reshapes the CIO role, it’s crucial first to distinguish between automation and autonomy. Think of automation as your trusty GPS navigation system: it reliably guides you along predetermined routes, step-by-step, removing the guesswork from your journey. It’s efficient, consistent, and predictable—but also limited to scenarios it’s programmed for. Autonomy, however, is more akin to a self-driving car. Not only does it navigate from point A to point B, but it also dynamically adapts in real-time, responding intelligently to unexpected obstacles, changes in weather, or traffic conditions. Autonomous systems don’t merely follow instructions—they independently analyze, decide, and continually learn from experience. For CIOs, this distinction matters profoundly. Transitioning from automation to autonomy isn’t simply an incremental upgrade—it’s a fundamental shift in how technology supports business strategy. CIOs must now lead organizations capable of embracing uncertainty, innovation, and real-time strategic decision-making powered by AI.
Generative AI Capabilities
Generative AI represents a remarkable advancement that fuels this transition from automation to autonomy. It moves beyond traditional algorithms by leveraging massive data sets to independently synthesize, interpret, and produce entirely new content and insights. Key capabilities include:
- Real-time Analytics: Instantly analyzing vast datasets to uncover hidden patterns, enabling proactive rather than reactive decisions.
- Autonomous Decision-making: Independently assessing complex scenarios and making nuanced, data-driven decisions without human intervention.
- Predictive Modeling: Accurately forecasting future trends, risks, and opportunities, significantly enhancing strategic planning and resource allocation.
Together, these capabilities mean CIOs are now positioned to lead at a higher strategic level, harnessing AI to drive innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
III. The Changing CIO Role – What, How, and Why?
What Changes?
As generative AI moves organizations beyond traditional automation, CIOs are experiencing profound shifts in their roles and responsibilities. Three core areas define this transformation:
- From Tactical to Strategic Leadership: Historically, CIOs were primarily responsible for overseeing technological infrastructure, managing systems, and ensuring operational efficiency. This tactical focus meant reacting to immediate IT needs and solving day-to-day operational challenges. Today, with generative AI driving autonomy, CIOs find themselves elevated into strategic leadership roles. They no longer simply manage technology but actively shape the broader organizational vision, using AI insights to influence long-term strategic planning, competitive positioning, and innovation. CIOs now sit at the decision-making table as indispensable strategic partners guiding the organization’s digital future.
- Increased Governance and Ethical Responsibilities: Generative AI’s powerful capabilities come with heightened responsibilities around governance, ethics, and compliance. CIOs must now ensure AI is deployed responsibly, transparently, and ethically. This means establishing robust governance frameworks, addressing biases, managing data privacy concerns, and complying with evolving regulatory standards. In essence, CIOs have become ethical stewards who safeguard organizational reputation and trust by managing the complex risks and implications introduced by autonomous systems.
- From Reactive Management to Proactive Innovation: Traditionally, CIOs responded reactively to business challenges—addressing issues as they arose. However, generative AI enables predictive modeling, real-time analytics, and autonomous decision-making. This shift empowers CIOs to move from reactive to proactive management. Rather than merely responding to technology problems, CIOs can now anticipate market trends, foresee operational disruptions, and identify strategic opportunities well before they manifest. Consequently, the CIO’s role evolves into one characterized by proactive innovation, foresight, and strategic agility, fundamentally changing how they contribute value to their organizations.
How It Changes?
As generative AI reshapes the CIO role, the nature of their responsibilities, required skills, and leadership style undergoes significant transformation. Specifically, CIOs experience change in three crucial ways:
- Expanded Responsibilities and Executive-Level Influence: Previously, the CIO’s role was primarily focused within IT boundaries, often isolated from broader business strategy. Now, generative AI-driven autonomy places CIOs squarely in the realm of strategic decision-making and business leadership. Their responsibilities have expanded beyond technology implementation to include strategic visioning, influencing corporate direction, and shaping innovation across the entire organization. As a result, CIOs increasingly participate at the executive and board level, acting as trusted strategic advisors whose insights influence decisions on investments, risk management, competitive positioning, and long-term growth strategies.
- Skillset Evolution and Team Development: The emergence of generative AI demands new skills and competencies from CIOs and their teams. Technical expertise, while still critical, now must be complemented by strategic thinking, ethical reasoning, innovation management, and advanced data literacy. CIOs must proactively lead talent development initiatives, ensuring their teams acquire necessary skills—ranging from AI governance to data science, strategic foresight, and agile methodologies. This evolution means CIOs themselves must continuously learn and adapt, embracing skills far beyond traditional IT management.
- Increased Cross-Functional Leadership: Generative AI’s cross-enterprise impact necessitates greater collaboration between technology and other business units. CIOs can no longer function purely within an IT silo; instead, they must actively lead cross-functional teams, breaking down organizational barriers to foster cooperation between IT, finance, marketing, operations, and even external stakeholders. This cross-functional leadership ensures AI initiatives align closely with organizational goals, improving business outcomes and enhancing organizational agility and innovation. CIOs become facilitators, collaborators, and connectors—critical roles in driving successful enterprise-wide generative AI adoption.
Why It Changes?
The role of the CIO is evolving significantly due to several powerful forces reshaping today’s business and technological landscape. Three primary factors explain why generative AI is prompting such transformative shifts in the CIO role:
- Rapid Technological Advancement: Generative AI represents one of the fastest-moving technological breakthroughs in recent history. Unlike incremental technology improvements, generative AI brings capabilities such as autonomous decision-making, real-time predictive analytics, and the ability to independently generate creative insights at unprecedented speeds. This rapid technological advancement demands that CIOs quickly adapt their leadership styles and strategies to harness the full potential of these transformative technologies effectively.
- Competitive Pressures and Business Demands: Today’s businesses operate in increasingly competitive markets characterized by constant disruption. Companies leveraging generative AI gain substantial competitive advantages through improved efficiency, innovation, and proactive decision-making. As a result, organizational leaders now expect CIOs not merely to manage technology but to actively drive competitive differentiation and business growth. CIOs must evolve from operational managers into strategic innovators, delivering measurable value directly linked to organizational success.
- Rising Governance, Ethical, and Regulatory Complexity: Generative AI’s immense potential also comes with considerable ethical, governance, and regulatory challenges. Organizations face heightened scrutiny over data privacy, fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI deployments. This increased complexity has reshaped the CIO role, placing CIOs at the forefront of navigating ethical considerations, establishing robust governance frameworks, and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations. These responsibilities demand a CIO who can confidently lead through uncertainty, balancing innovation with risk management, and ethical responsibility with competitive advantage—further underscoring why the CIO role must adapt significantly in this new AI-driven era.
Table: Generative AI Impact on CIO Role
| Generative AI Capabilities | Impact on CIO Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Real-time Data Synthesis & Advanced Analytics | Enables CIOs to proactively inform strategic business decisions using accurate, real-time insights rather than retrospective data. |
| Autonomous Decision-making | CIOs shift from overseeing routine tasks to ensuring AI-driven decisions align with ethical standards, compliance, and corporate strategy. |
| Personalization & Adaptive Content Generation | CIOs lead initiatives to enhance user experience, employee productivity, and customer engagement through tailored, AI-driven content. |
| Predictive Modeling & Forecasting | CIOs transition into strategic advisory roles, leveraging precise AI forecasting to optimize resource allocation, investments, and risk management. |
| Automated Innovation & Design Exploration | Empowers CIOs to accelerate innovation cycles, streamline product development, and lead cross-functional teams in exploring new opportunities rapidly and efficiently. |
| Natural Language Processing & Generative Communication | CIOs enhance internal and external communications, improving transparency, stakeholder engagement, and employee satisfaction with AI-generated content. |
| Operational Efficiency through Autonomous Systems | Allows CIOs to significantly reduce operational overhead, reallocating IT resources toward strategic initiatives, innovation, and digital transformation. |
| Governance and Ethical Oversight | Places CIOs at the forefront of AI governance, ensuring transparency, fairness, compliance, and managing ethical concerns proactively using recognized standards (e.g., COBIT, NIST). |
This clear mapping helps CIOs visualize exactly how generative AI reshapes their role from technology enablers to strategic business leaders.
IV. CIO Archetypes Emerging from Generative AI
The transformative impact of generative AI has led to the emergence of distinct CIO archetypes. Each archetype reflects different approaches, priorities, and organizational contexts shaped by AI maturity, strategic alignment, and cultural readiness. Understanding these archetypes helps CIOs recognize their own leadership style, strengths, and areas for strategic development.
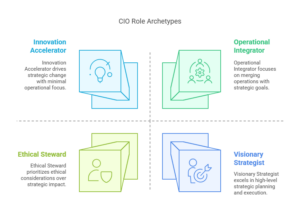
Four Emerging CIO Archetypes:
- Visionary Strategist
- Ethical Steward
- Innovation Accelerator
- Operational Integrator
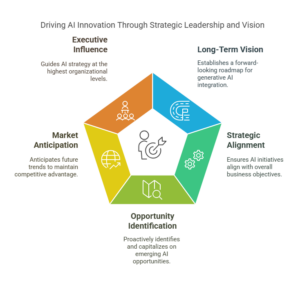
1. Visionary Strategist
The Visionary Strategist is a forward-thinking leader who sets a compelling, long-term vision for generative AI and aligns it seamlessly with the organization’s broader business strategy. This archetype proactively identifies emerging opportunities, anticipates future market trends, and positions the organization to leverage AI-driven competitive advantages. The Visionary Strategist holds significant influence at executive and board levels, articulating the strategic importance of generative AI clearly and persuasively, guiding the entire organization toward a cohesive and innovative AI future.
Characteristics:
- Focuses on strategic alignment of generative AI with long-term business goals.
- Actively involved in executive leadership and board discussions.
- Champions generative AI initiatives, proactively driving adoption at a strategic level.
Factors Driving this Archetype:
- Strategic Alignment: High
- AI Maturity: Moderate to High
- Organizational Adoption: Strategic and transformative
Key Responsibilities:
- Align generative AI initiatives with organizational strategic objectives.
- Clearly articulate and communicate a compelling long-term vision.
- Influence senior leadership and actively participate in executive decision-making.
Example Behavior:
- Setting clear generative AI-driven business objectives at the board level.
- Anticipating market shifts and positioning the organization for competitive advantage through AI.
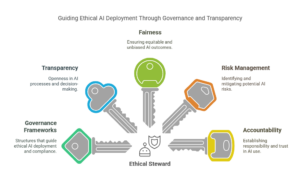
2. Ethical Steward
The Ethical Steward emphasizes responsible, ethical, and compliant deployment of generative AI technologies. This archetype leads with a strong focus on governance frameworks, transparency, fairness, and risk management, ensuring AI aligns with organizational values and ethical standards. The Ethical Steward navigates complex regulatory environments, establishes accountability structures, and proactively manages potential biases, privacy concerns, and societal implications arising from AI adoption.
Characteristics:
- Prioritizes robust governance frameworks and ethical standards for AI.
- Proactively manages risks related to bias, compliance, and data privacy.
- Serves as a voice of caution and integrity in AI deployment.
Factors Driving this Archetype:
- AI Maturity: Medium to High
- Governance Readiness: Very High
- Organizational Risk Profile: Highly regulated industries (finance, healthcare)
Key Responsibilities:
- Develop and oversee robust governance and ethical frameworks.
- Ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI-driven decision-making.
- Manage compliance, regulatory alignment, and risk mitigation effectively.
Example Behavior:
- Ensuring thorough reviews and audits of AI systems.
- Embedding responsible AI principles deeply into corporate governance frameworks.
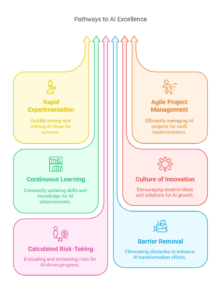
3. Innovation Accelerator
The Innovation Accelerator thrives on rapid experimentation, agile project management, and continuous learning to quickly scale successful generative AI projects across the enterprise. This archetype fosters a culture of innovation, encourages calculated risk-taking, and proactively removes organizational barriers to accelerate AI-driven transformation. Innovation Accelerators excel in environments characterized by intense competition, fast-paced technological evolution, and the continuous pursuit of new growth opportunities.
Characteristics:
- Emphasizes rapid experimentation, agile project deployment, and iterative learning.
- Drives generative AI adoption at the operational level, focusing on quick wins and tangible results.
- Supports a culture of continuous innovation, agility, and risk-taking.
Factors Driving this Archetype:
- AI Adoption Pace: Rapid and iterative
- Organizational Culture: Innovative, adaptive, and agile
- Business Pressure: High competition requiring continuous innovation
Key Responsibilities:
- Rapidly pilot, test, and scale generative AI initiatives.
- Foster an agile, experimental, and adaptive organizational culture.
- Encourage cross-functional collaboration and quick iteration cycles.
Example Behavior:
- Quickly piloting generative AI projects, scaling successful pilots across business units.
- Encouraging bottom-up innovation and embracing experimentation.
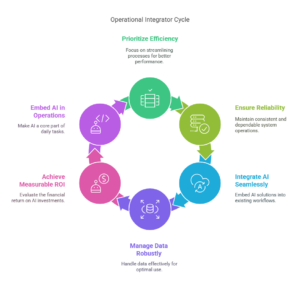
4. Operational Integrator
The Operational Integrator prioritizes efficiency, reliability, and operational excellence, seamlessly integrating generative AI into existing systems and workflows. This archetype focuses on scalable infrastructure, robust data management, interoperability, and measurable ROI, ensuring that generative AI solutions are practical, dependable, and deeply embedded within daily operations. Operational Integrators are critical in organizations where technological stability, predictable performance, and consistent results form the basis for long-term success.
Characteristics:
- Focuses on the operational integration and efficiency of AI systems.
- Ensures smooth implementation, seamless interoperability, and scalable infrastructure.
- Prioritizes stability, reliability, and ROI through operational excellence.
Factors Driving this Archetype:
- Technological Infrastructure: Strong emphasis on scalability, integration, and efficiency.
- AI Maturity: Moderate, often early-stage adoption
- Organizational Focus: Efficiency and cost reduction
Key Responsibilities:
- Ensure smooth operational integration and scalability of generative AI technologies.
- Manage infrastructure reliability, performance, and interoperability.
- Continuously optimize AI deployments for measurable operational effectiveness and cost efficiency.
Example Behavior:
- Integrating AI capabilities into existing systems for maximum operational efficiency.
- Prioritizing investments in robust, scalable infrastructure and reliable performance metrics.
Table: Emerging CIO Archetypes
| Archetype | Key Drivers | Primary Characteristics and Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Visionary Strategist | High strategic alignment, strong executive support, transformative organizational culture | Shapes and communicates long-term AI vision, drives strategic business alignment, influences executive-level decisions |
| Ethical Steward | High governance complexity, regulatory pressures, risk-sensitive industries (e.g., finance, healthcare) | Leads ethical AI governance, ensures compliance and fairness, manages AI-related risks, establishes transparent accountability frameworks |
| Innovation Accelerator | Rapid adoption pace, innovative and agile culture, high competitive pressures | Champions rapid experimentation, agile pilots, iterative innovation, quickly identifies and scales successful generative AI projects across business units |
| Operational Integrator | Moderate AI maturity, strong infrastructure capability, efficiency-focused culture | Ensures smooth integration and scalability of AI systems, emphasizes operational excellence, reliability, and measurable ROI, manages infrastructure efficiently |
Understanding these archetypes helps CIOs more clearly identify their leadership strengths, focus strategic efforts effectively, and guide their organizations confidently through the transformative potential of generative AI.
These four archetypes, while highlighted by the rapid rise of generative AI, represent enduring and recommended CIO roles crucial for navigating broader digital transformation and technological evolution. Driven by increasing data complexity, disruptive innovation, and evolving governance demands, these roles provide a strategic foundation for CIOs to lead effectively, both in the current landscape and in managing future technology transformations beyond AI. Generative AI sharply accelerates existing trends, bringing these responsibilities into clear focus, but their applicability extends far beyond this specific technology.
Table: Factors Driving Emerging CIO Archetypes
| Archetype | Strategic Alignment | AI Adoption Pace | AI Maturity Level | Governance & Ethics | Organizational Culture | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visionary Strategist | Very High | Strategic & Measured | Moderate to High | High | Transformational | Strategic AI alignment and long-term vision. |
| Ethical Steward | High | Moderate & Cautious | Medium to High | Very High | Risk-aware & regulated | Ethical AI governance, compliance, and risk mitigation. |
| Innovation Accelerator | Moderate to High | Rapid & Iterative | Variable (often medium) | Moderate | Agile & Innovation-driven | Quick pilots, experimentation, and rapid scaling. |
| Operational Integrator | High | Moderate & Steady | Moderate | Moderate to High | Efficiency-driven | Operational excellence, integration, and scalable infrastructure. |
Explanation of Drivers:
- Strategic Alignment: The clarity and strength of connection between AI strategy and broader organizational goals.
- AI Adoption Pace: Speed and approach toward deploying and scaling AI initiatives.
- AI Maturity Level: The sophistication, readiness, and experience level the organization currently has with AI technologies.
- Governance & Ethics: How rigorously the organization manages risks, ethical concerns, and compliance related to AI.
- Organizational Culture: The prevailing attitudes toward innovation, risk-taking, agility, and transformation.
- Primary Focus: The core responsibility and orientation shaping the CIO role within the AI-driven context.
V. Real-world Case Studies and Industry Examples
Generative AI is already demonstrating transformative impact across diverse industries, highlighting practical, measurable successes. These case studies illustrate how CIOs in different sectors leverage generative AI to drive strategic advantage, efficiency, and innovation:
1. Finance: JPMorgan
JPMorgan uses generative AI to significantly enhance forecasting accuracy. By deploying AI-driven analytics, they’ve improved the precision of their financial predictions by approximately 30%, enabling proactive, informed investment decisions, reducing risk exposure, and driving strategic growth in volatile markets.
2. Healthcare: Mayo Clinic
At the Mayo Clinic, generative AI has dramatically reduced diagnosis timelines—cutting the diagnostic process by up to 50% in certain medical contexts. This accelerates personalized treatment plans, enhances patient outcomes, and substantially improves clinical efficiency, underscoring the profound impact AI-driven autonomy has on healthcare.
3. Retail: Zara
Fashion retailer Zara leverages generative AI to predict and respond to evolving fashion trends more accurately. This approach has allowed Zara to optimize inventory management, reducing excess stock by roughly 25%, translating into substantial cost savings, minimized waste, and improved responsiveness to consumer demand.
4. Manufacturing: Autodesk
Autodesk incorporates generative AI into its product design processes through generative design software. This AI-driven approach explores thousands of design permutations within defined parameters, resulting in up to 20% reduction in production costs and 15% improvement in product performance and quality, significantly streamlining innovation cycles.
5. Education: Houston ISD
The Houston Independent School District (HISD) utilizes generative AI to enhance personalized learning. Through partnerships leveraging generative AI, HISD generates over 2,200 tailored reading passages daily for grades 3-10, closely aligned with educational standards, improving student engagement, learning outcomes, and instructional effectiveness.
6. Entertainment: Lionsgate
Lionsgate Entertainment, known for blockbuster franchises, is partnering with generative AI startups to streamline movie and television production processes. AI-assisted storyboarding and editing tasks have accelerated pre-production workflows, significantly improving efficiency, creativity, and resource allocation, potentially saving millions of dollars in production costs.
7. Hospitality: Criterion Hospitality
Criterion Hospitality has successfully integrated AI-powered kiosks and chatbots into daily operations, greatly enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency. The result has been a notable reduction—approximately 66%—in staffing needs for routine customer service tasks, allowing human resources to focus on higher-value, strategic activities that directly improve guest satisfaction. These examples demonstrate how generative AI is actively reshaping industries, positioning CIOs at the strategic forefront, and delivering measurable business value across the board.
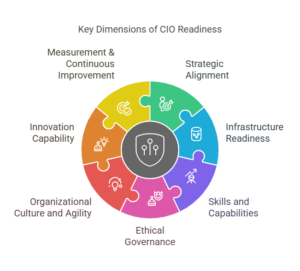
VI. Assessing CIO Readiness for the Generative AI Shift
Effectively leading an organization through the shift from automation to autonomy requires CIOs to be prepared across several critical dimensions. Assessing readiness involves carefully examining capabilities, culture, and strategic alignment. Below are the key dimensions and representative questions to help CIOs evaluate their readiness for adopting generative AI.
The shift from automation toward autonomy driven by generative AI isn’t merely about implementing new technology; it demands a complete transformation of strategy, capabilities, leadership style, and organizational culture. Given these significant implications, CIOs must methodically evaluate their organization’s readiness to successfully navigate this transition.
Below, we elaborate on seven critical dimensions for assessing CIO readiness. Each dimension provides clear insights into your organization’s preparedness, highlighting both strengths and gaps that require attention.
1. Strategic Alignment
Ensuring AI initiatives directly support broader business objectives.
Why this matters:
Strategic alignment ensures generative AI efforts directly contribute to core business objectives, not existing as isolated or peripheral initiatives. It measures the CIO’s effectiveness in linking AI strategy to broader organizational outcomes.
Indicators of strong strategic alignment include:
- Clearly articulated generative AI objectives integrated into the corporate strategy.
- Executive-level buy-in and strategic investment in AI initiatives.
2. Infrastructure Readiness
Having robust, scalable technology infrastructure and high-quality data.
Why this matters:
Infrastructure readiness is fundamental to effectively deploying and scaling generative AI systems. High-quality data, robust data governance, and scalable technology infrastructure significantly accelerate and facilitate successful AI adoption.
Indicators of infrastructure readiness include:
- Comprehensive, high-quality data repositories.
- Flexible, cloud-based infrastructure capable of supporting complex AI computations.
- Mature data governance and management practices.
3. Skills and Capabilities
Developing the right talent, technical and strategic skills to deploy and manage generative AI.
Why this matters:
The rapid technological advancements of generative AI create significant skill gaps within most organizations. CIOs must proactively address these gaps through strategic recruitment, targeted training, and continuous skill development programs.
Indicators of skill readiness include:
- Clearly defined skill gap analysis and targeted reskilling programs.
- Robust training frameworks supporting continuous learning in AI and related technologies.
- A strong talent pipeline and development pathways for strategic AI roles.
4. Ethical Governance
Establishing strong ethical and regulatory governance frameworks to manage AI responsibly.
Why this matters:
Generative AI carries significant ethical, regulatory, and reputational risks. Strong ethical governance demonstrates the organization’s commitment to responsible AI, transparency, fairness, and compliance—critical factors in maintaining trust and competitive positioning.
Indicators of ethical governance include:
- Defined ethical AI principles and policies.
- Established governance frameworks like COBIT or IEEE’s Ethically Aligned Design.
- Transparent accountability and oversight structures addressing AI-related risks.
5. Organizational Culture and Agility
Fostering an innovative culture open to experimentation, rapid iteration, and learning.
Why this matters:
Generative AI thrives in an environment of experimentation, innovation, and rapid adaptability. Organizations with agile cultures and a willingness to embrace new technologies are far better positioned to capitalize on AI’s strategic benefits.
Indicators of a supportive culture include:
- Openness to experimentation and calculated risk-taking.
- Demonstrable track record of successful technology-driven change initiatives.
- Clear leadership support for innovation and cultural transformation.
6. Innovation Capability
Capability to quickly pilot, learn, adapt, and scale AI-driven innovation across the organization.
Why this matters:
Effective use of generative AI requires the capability to swiftly pilot new solutions, iterate rapidly, and scale successful projects across business units. CIOs must evaluate how effectively their teams can move from idea to implementation.
Indicators of innovation capability include:
- Agile project management and innovation frameworks (e.g., Lean Startup methodologies, Design Thinking).
- Ability to rapidly prototype, test, evaluate, and scale AI-driven innovations.
- Cross-functional collaboration capabilities and streamlined innovation processes.
7. Measurement & Continuous Improvement
Implementing clear KPIs, metrics, and processes to measure AI effectiveness and continuously refine initiatives.
Why this matters:
Continuous improvement through rigorous performance measurement is essential for sustaining AI effectiveness over time. CIOs must build clear, measurable KPIs and feedback loops to continuously refine strategies based on real-world outcomes.
Indicators of strong measurement practices include:
- Clearly defined and widely communicated KPIs.
- Regular monitoring, analysis, and reporting of AI project results.
- Demonstrable iterative improvements based on structured feedback processes.
How CIOs Can Use This Framework
By carefully examining these seven dimensions, CIOs gain a clear and comprehensive understanding of their readiness to successfully lead the transition toward autonomy through generative AI. Each dimension provides strategic direction, highlighting where immediate improvements can be made, which gaps must be addressed, and how effectively the organization is positioned to fully capitalize on AI-driven innovation and competitive advantage.
Conducting a systematic assessment using these criteria allows CIOs to move beyond mere technology adoption, shaping their organizations into agile, innovative, and ethically responsible leaders in the generative AI era.
Sample Readiness Assessment Questions & Interpretation:
1. Strategic Alignment
- Question: “How closely are our generative AI projects aligned with our organization’s overall strategic objectives?”
- Interpretation: Clear alignment indicates readiness and strategic clarity. Weak alignment suggests a need for more strategic integration.
2. Infrastructure Readiness
- Question: “Do we have the necessary data infrastructure—quality, governance, and scalability—to fully leverage generative AI?”
- Interpretation: A strong infrastructure shows readiness to rapidly implement generative AI. Gaps here signal a need for targeted infrastructure investments.
3. Skills and Capabilities
- Question: “Have we clearly identified skill gaps and implemented structured training programs to prepare our team for generative AI?”
- Interpretation: A proactive approach to skills indicates readiness; lack of clear skill development plans may limit successful adoption.
4. Ethical Governance
- Question: “Are our governance frameworks sufficient to manage ethical concerns, biases, and regulatory compliance associated with generative AI?”
- Interpretation: A robust governance framework demonstrates ethical readiness; absence or limited frameworks indicates significant risks that must be addressed.
5. Organizational Culture and Agility
- Question: “Does our organizational culture actively support experimentation, agility, and rapid adoption of generative AI initiatives?”
- Interpretation: A positive culture toward innovation signifies strong readiness; resistance or slow adaptability signals cultural barriers that require leadership attention.
6. Innovation Capability
- Question: “Can we quickly pilot generative AI initiatives, scale successes, and effectively integrate lessons learned into our ongoing operations?”
- Interpretation: High capability for agile innovation indicates readiness for accelerated AI transformation; limited capability suggests necessary improvements in innovation processes.
7. Measurement & Continuous Improvement
- Question: “Have we clearly defined metrics to evaluate the success of our generative AI initiatives, and do we consistently refine based on measured outcomes?”
- Interpretation: Clearly defined, regularly monitored metrics indicate readiness for continuous improvement. Lack of metrics or inconsistent tracking highlights significant gaps in strategic management.
Using these questions to critically evaluate readiness helps CIOs effectively lead the transition toward AI-driven autonomy, proactively addressing areas requiring attention to ensure sustainable and impactful generative AI adoption.
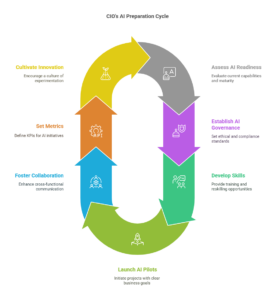
VII. Seven Actions CIOs Must Take to Prepare
Generative AI’s transformative potential necessitates proactive preparation. CIOs should take these seven critical actions to successfully guide their organizations toward strategic autonomy, innovation, and competitive advantage:
1. Conduct a Strategic AI Readiness Assessment
Start by thoroughly evaluating your organization’s current capabilities, infrastructure readiness, and AI maturity level. This includes assessing data quality, technological scalability, and the existing skill sets within your teams. Understanding your baseline maturity allows you to strategically identify where investments, upgrades, or talent development may be needed.
2. Establish Comprehensive AI Governance and Ethical Frameworks
To responsibly deploy generative AI, establish clear, robust governance and ethical frameworks. Define accountability structures, ethical guidelines, and compliance processes to manage potential risks like biases, privacy concerns, and regulatory issues proactively. Well-defined frameworks build trust internally and externally, ensuring your AI initiatives remain sustainable, ethical, and compliant.
3. Invest in Continuous Skills Development and Team Reskilling
Generative AI demands new competencies. Continuously evaluate your team’s evolving skill gaps and provide structured learning pathways, training programs, certifications, and reskilling initiatives. Prioritize both technical skills (AI, data science, analytics) and strategic capabilities (critical thinking, ethics, leadership) to equip your team for successful AI adoption and innovation.
4. Launch Strategic AI Pilot Projects with Clear Business Objectives
Initiate focused, manageable pilot projects that demonstrate clear business value. Choose use cases aligned with organizational priorities, such as improving forecasting accuracy or customer experience. These pilot initiatives provide tangible “quick wins,” build credibility, validate ROI, and help secure executive and organizational buy-in for broader AI transformation.
5. Develop Cross-functional Collaboration and Communication Structures
Generative AI requires strong alignment across diverse business functions. Develop clear communication channels, joint governance teams, and collaborative processes involving IT, finance, operations, marketing, HR, and legal departments. Cross-functional collaboration ensures strategic alignment, enhances operational effectiveness, and accelerates AI integration throughout the organization.
6. Set Up Robust Metrics and Continuous Improvement Mechanisms
Establish clear, measurable KPIs and metrics to assess the effectiveness, efficiency, and strategic impact of your AI initiatives. Regularly monitor progress, gather insights, and continuously refine your strategies based on measured outcomes. Transparent metrics facilitate accountability, foster continuous improvement, and drive ongoing organizational commitment to generative AI.
7. Build a Culture of Innovation and Agile Experimentation
Finally, nurture an organizational culture where innovation, experimentation, and agility thrive. Encourage rapid prototyping, iterative learning, and scaling successes quickly across the organization. Reward calculated risk-taking, celebrate innovative thinking, and maintain openness to adapt and pivot rapidly, positioning your teams to capitalize effectively on generative AI opportunities. By proactively implementing these seven strategic actions, CIOs will not only prepare their organizations for generative AI’s profound impacts but also position themselves as critical strategic leaders driving innovation and competitive differentiation into the future.
VIII. Conclusion
Generative AI isn’t merely another incremental technology advancement—it represents a profound transformation in how organizations operate, compete, and innovate. CIOs who proactively embrace this shift from automation to autonomy will position themselves not merely as technology stewards but as strategic leaders, ethical guardians, and catalysts of innovation across their organizations. The strategic, operational, and ethical responsibilities that accompany generative AI adoption demand that CIOs clearly assess their readiness and actively define their leadership archetype. Whether you resonate most with the Visionary Strategist, Ethical Steward, Innovation Accelerator, or Operational Integrator, recognizing your archetype empowers you to maximize your leadership impact and strategically guide your organization into this new era of AI-driven autonomy. Now is the time to critically assess your organization’s generative AI readiness. Define your archetype clearly, close capability gaps proactively, and commit to the transformative actions outlined. By doing so, you won’t just adapt to generative AI—you’ll harness its full potential to drive sustained innovation, competitive advantage, and strategic value for your organization’s future.
Are you ready to lead your organization into the autonomous future powered by generative AI?